As marketing, you are only positioned to create convincing use cases to dismantle customer data silos. Your in -depth understanding of customer behavior, the interfunctional perspective and the ability to demonstrate the tangible commercial impact make you a key player in this effort. MARTECH – that you select, make it possible or manage these platforms – gives you another way to lead to use customer data.
Customer -centered perspective
You have a holistic vision of the customer journey which goes beyond the creation of promotional campaigns or the generation of prospects. This allows you to:
- Identify the painful points caused by fragmented data: Quantify these points of pain by estimating the loss of income or the negative impact on marketing processes, such as the longer market delay for new campaigns.
- Illustrate how the integrated data improves customer experiences: Demonstrate gains through unlocked income opportunities, an increase in customer satisfaction scores or a decrease in complaints and abandonment of baskets.
- Display the value of a unified customer view through the contact points: Integration of data sources can improve engagement and conversion rates.
Interfunctional ideas
Your collaboration with various departments allows you to:
- Highlight interdependencies between different data sources: Show how Customer Silos data have a negative impact on marketing processes and hinder customer experience improvements.
- Demonstrate how the integrated data improves collaboration: Better data management helps you to become a stronger partner in other teams and to appropriate customer data.
- Identify cross -selling and selling opportunities at the level: This is particularly useful for companies with several commercial units, guaranteeing cross -selling opportunities on different products of products or services.
Quantifiable commercial impact
You can create use cases which demonstrate a clear return on investment (king), as shown in these areas:
- Campaign performance improvement: Better targeting and personalization improve marketing efficiency.
- Increased life value of the customer: More relevant interactions lead to deeper customer relationships.
- Cost savings: The elimination of redundant or ineffective marketing efforts rationalizes operations and maximizes budgets.
Dig more deeply: 5 things that marketing specialists can do to abolish data silos
Data -based decision -making
As a marketing specialist, you should be at the forefront of customer data expression for strategic decisions:
- More precise perfections and predictions: The integrated data allow a more intelligent decision -making.
- Greatest agility in marketing strategies: Access to real -time data allows faster pivots and adjustments.
- Improved AI capacities and automatic learning: Complete data sets feed more efficient automation and predictive modeling.
Compliance and confidence
You must understand the importance of data confidentiality and:
- Illustrate how integrated data management improves compliance efforts: Correctly structured data help meet regulatory requirements.
- Show how to improve data governance strengthens customer confidence: Transparent and secure data management increases consumer confidence.
- Demonstrate the value of consent management through contact points: Ensure alignment with your business privacy policies maintains the use of ethical data.
By creating these use cases, you can effectively plead to dismantle it from data silos, benefiting not only to marketing but to the entire organization. Although this process may seem simple, it is complex – especially when several silos exist. However, taking up this challenge leads to an improvement in customer experiences, more efficient operations and better commercial results.
Dig more deeply: Decompose data silos: a practical guide to integrated marketing data
5 elements to be included in the use of customer data
When developing use cases, make sure they include these five elements:
1. Remove the commercial impact
Create profitability analyzes that quantify the cost of data silos and show how to decompose them benefit the company.
- Highlight the lost opportunities due to fragmented data.
- Show how unified data improves marketing efficiency and return on investment.
- Demonstrate the impact on customer engagement and conversion rates.
2. Improvement of collaboration in a cross team
Your use cases can promote collaboration by:
- Encourage teams to define which data fields should come from each source.
- Improvement of the customer experience with integrated information.
- Improve marketing processes by taking advantage of the data from several departments.
3. Improve customer ideas
User cases help refine customer information:
- More specific customer profiles.
- Best customization of marketing campaigns.
- Improved targeting of good accounts and individuals within organizations.
4. Optimization of marketing performance
Unified data allow you to:
- Reduce the marketing time for campaigns.
- Improve the monitoring of the customer journey.
- Make data -based decisions to optimize real -time marketing strategies.
5. Drive an organizational change
Defend data integration by:
- Demonstrating its positive impact on internal marketing processes.
- Helping stakeholders understand how silos are hampering commercial objectives.
- Support the allocation of resources for multidisciplinary teams working on data unification.
Dig more deeply: How to relax your organization and be more focused on customers
Measure the advantages
Here are key measurements you can use to assess the advantages of dismantling customer data silos:
- Income growth over a specific period.
- Increase in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improvements of marketing efficiency (for example, reduction in brand delay, decrease in supplier dependence).
- Higher conversion rate and customer value for life.
- A better return to advertising expenses (ROAS) and acquisition costs for lower customers.
- Access to relationships and dashboards in real time for continuous monitoring.
How to start with use cases
When making a use case, start with a simple declaration that helps stakeholders – in particular technical teams – Understanding the advantages:
- “By (describe the use case), we can (explain how it benefits customers). This will have an impact on our commercial objectives by (list the advantages). »»
Example:
“The combination of preferences from self-detached customers with the behavior of the past website allows us to personalize e-mails of electronic commerce. This will increase open and click rates, leading more customers to our product pages. In turn, this supports the annual income target of our company. In addition, this use case allows the marketing team to set up personalized messaging campaigns without additional investment using a dynamic model filled with customer data. »»
Clearly state the expected commercial impact helps to prioritize different use cases. Avoid adding technical or operational details. These must be managed by the teams concerned according to commercial requirements.
You can also provide a context and refine use cases in collaboration with other teams as you develop them.
Prioritize use cases
Once the use cases have been created, you can help prioritize them using the following prioritization framework.
- Axis X: Implementation difficulty.
- Y axis: Commercial impact.
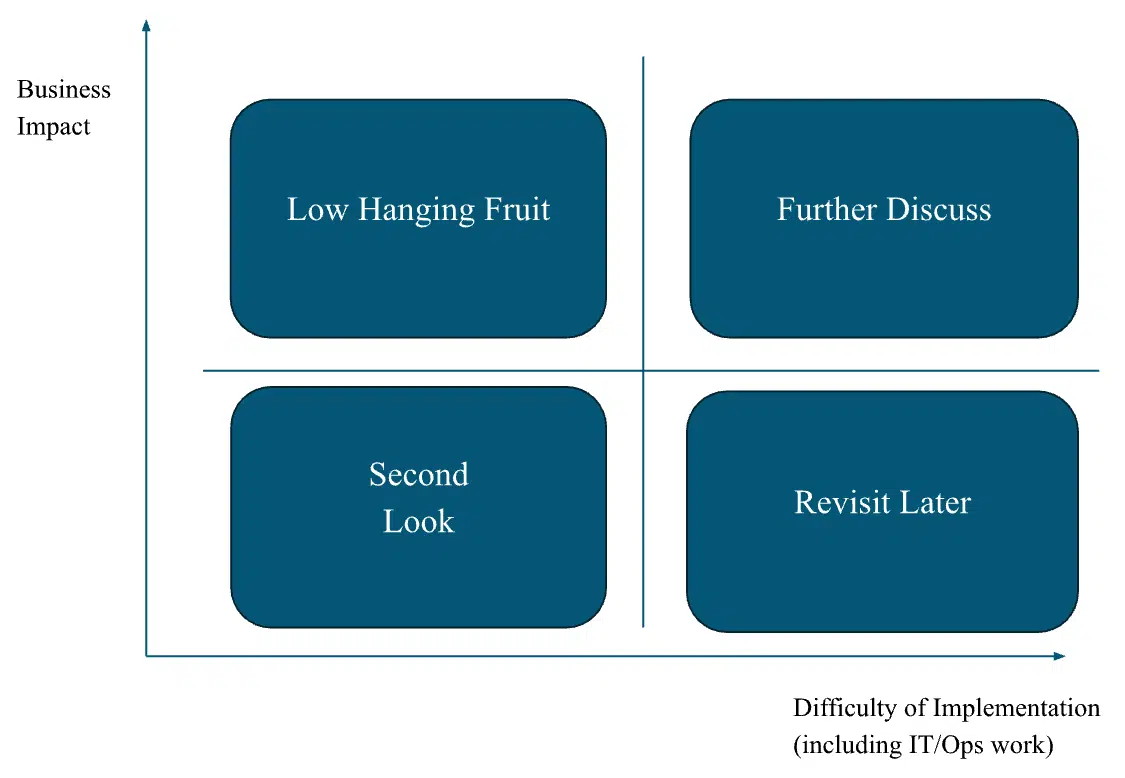
- Low prices: Easy to implement use cases which have a high commercial impact must be priority first. These offer quick victories with a minimum of effort.
- Second look: These are easier to implement but have a lower commercial impact. Although not all of them are being prosecuted immediately, consider selecting small fast victories – especially those closer to the top of this quadrant.
- Discuss: These use cases have a high commercial impact, but are more complex to implement. Prioritize the simplest first. Regular discussions with technical teams can help determine the best approach.
- Revisit later: These use cases are both difficult to implement and have an immediate lower commercial impact. However, they must be examined periodically, as technological changes or commercial priorities can make them more viable in the future.
In addition, you will have to balance between prioritizing a rapid victory with a low effort compared to the investment in a more complex case of use which could give a more important long -term impact. The regular update and reassessment of the position of use cases in this context guarantee that your marketing efforts remain aligned on commercial objectives.
Dig more deeply: How the objectives and shared incentives improve marketing results
The contributory authors are invited to create content for Martech and are chosen for their expertise and their contribution to the Martech community. Our contributors work under the supervision of editorial And contributions are verified for quality and relevance for our readers. The opinions they express are theirs.
👑 #MR_HEKA 👑



